Cases when an Eway bill is not required
Cases when an Eway bill is not required
The GST law was introduced in India to right the several wrongs that the erstwhile law had. One of the main problems was that there was lack of transparency in the process with respect to both, the taxpayers as well as the Government. Under the GST regime, one of the methods of the Government to ensure transparency is by digitizing the process. Eway bill is one such measure.
1. Documents to carry in case eway bill is not required
An Eway bill will act as an effective tool to check on tax evasion at various points and to track the movement of goods. But when it is not required to be generated, the transporter has to ensure that a copy of tax invoice or a bill of supply prepared according to the provisions of Law is carried.
An insight of how eway bill acts as a tax evasion tool can be seen from an instance. If some raw material is being transported from Karnataka to Tamil Nadu where it is processed into finished goods and sold, the state which the should receive the revenue is Tamil Nadu because it is the state of consumption.
Whereas, if half of the finished goods are transported to another state, say Kerala and then sold there, then the revenue belongs to Kerala as well. This is where the Eway bill comes into use. It helps us to clearly know the movement of goods at every state and thus helps prevent tax evasion.
Hence, Eway bill is an important document that facilitates movement of goods from one place to another. This ‘document’ can be generated electronically by uploading relevant details which include the type of goods, the HSN code, quantity and taxable value, details of the recipient, details of the transporter, vehicle number etc. An Eway bill must be generated before the movement of goods commences.
Therefore, it is needless to say that if a taxpayer is covered under mandatory provisions, the goods should, at all times be covered by an Eway bill. But if not, then he is required to carry cop of tax invoice or the valid document stated under the Invoicing provisions of GST laws.
2. Specific goods exempted from eway bill
Specific goods that are exempt from eway bill rules are:
- Transportation of those goods laid down in the annexure to rules as specified below:
- Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to household and non-domestic exempted category customers
- Kerosene oil sold under PDS
- Postal baggage transported by Department of Posts
- Natural or cultured pearls and precious or semi-precious stones; precious metals and metals clad with precious metal
- Jewellery, goldsmiths’ and silversmiths’ wares and other articles
- Currency
- Used personal and household effects
- Unworked and worked coral
- Goods being transported are alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum crude, high-speed diesel, petrol, natural gas or aviation turbine fuel.
- Goods being transported are not treated as supply under Schedule III of the Act (Schedule III consists of activities that would neither be supply of goods nor service like service of an employee to an employer in the course of his employment, functions performed by MP, MLA etc.)
- Goods transported are empty cargo containers
- Goods, other than de-oiled cake, being transported are specified in notification No. 2/2017– Central tax (Rate) dated the 28th June, 2017. Few of the goods that are included in the above notification are as follows:
- Curd, lassi, buttermilk
- Fresh milk and pasteurized milk not containing added sugar or other sweetening matter
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Unprocessed tea leaves and unroasted coffee beans
- Live animals, plants and trees
- Meat
- Cereals
- Unbranded rice and wheat flour
- Salt
- Items of educational importance (books, maps, periodicals)
- Goods exempted under notification No. 7/2017– Central Tax (Rate) dated 28th June 2017 (supply by CSD to unit run canteens and authorized customers) and notification No. 26/2017– Central Tax (Rate) dated 21st September 2017 (consists of heavy water and nuclear fuels)
3. Specific transactions that do not require eway bill
Other transactional cases where eway bill is not required are:
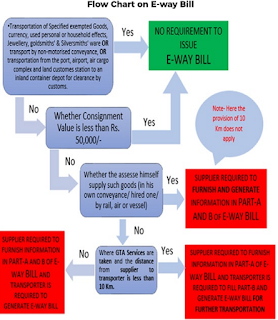
- eway bill is optional for Goods of value less than Rs. 50,000 (except in cases of mandatory Eway bill provisions like the movement of Handicraft goods and movement of goods for Inter-state Job work )
- If Goods are being transported by a non- motorised conveyance (Ex. Horse carts or manual carts)
- If Goods are being transported:
- From the port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot (ICD) or a container freight station (CFS) for clearance by Customs
- From ICD or CFS to a customs port, airport, air cargo etc under customs bond
- From one customs port/station to another one under customs bond
- Goods transported under the customs supervision or customs seal
- Goods transported within the notified area
- Goods transported are transit From/ to Nepal/ Bhutan
- If Goods are transported to a weighbridge within 20kms and back to the place of business by being covered under a Delivery Challan
- Where Government or local authorities transport goods by rail as a consignor
- Goods transported are to/from the Ministry of Defence
So, if a taxpayer falls under any of the above categories, he will not be required to generate an E-way bill. Though the taxpayers who fall under E-way bill exemptions are relieved of this compliance, they should ensure that the other documents like the invoice and bill of supply are in accordance with the rules and regulations.
(Sources : tax websites)
Comments
Post a Comment